
July 10, 2018 in Advisory Notes
Heat Pumps for Carbon Neutral Heating
Heat pumps are a well-established technology that can provide a pathway toward on-site carbon neutrality not possible in buildings that rely on gas fo...
July 19, 2016
New electrical network tariff charges will encourage many businesses to review energy usage and ways they can reduce their operational costs.
Electricity supply companies are moving customers onto tariff structures that more accurately reflect the electrical demand placed on the supply network. Customers in Victoria have now joined compatriots in NSW, the ACT and QLD where tariff changes have already taken place.
Previously, electrical usage demand charges were based on the connected electrical load measured in kilowatts (kW) (also known as Real Power or Working Power or Actual Power or Active Power). Demand charges were usually based on the highest demand measured within a 12 ‘rolling’ month period.
The new tariff approach uses a kilovolt-amp (kVA) (also known as Total Power or Apparent Power) maximum demand tariff charge which is reliant on power factor.
Total Power (kVA) x power factor = Real Power (kW)
What is Power factor?
In simple terms, power factor is the measure of how efficiently incoming power is used. Inefficient use is caused by inductive loads within the electrical installation, such as transformers, induction motors, and fluorescent lighting, which require real power [kW] as well as reactive power [kVAr] to maintain electromagnetic fields that are required for their operation.
The higher the reactive power used, the larger the inefficiency caused within the distribution network. Electricity supply companies seek to encourage customers to improve the efficiency, or power factor, of their facility by penalising inefficient usage with higher charges. A power factor of 1.0 means 100% of the supply is being used efficiently, a power factor of 0.5 means the use of the power is very inefficient.
Power Factor Correction
Customers can install power factor correction equipment to help improve their power factor and thereby lower their electricity costs. The installation of appropriate power factor correction equipment can result in typical payback periods of between two and three years, with an expected equipment lifecycle in the order of 15 to 20 years.
Other benefits of power factor correction include the ability to increase the electrical capacity within a facility, and improvements to the voltage supply to equipment, which can increase plant life.
Power factor correction equipment is essentially a capacitor bank that stores and provides reactive power when required. This equipment can be installed on particular pieces of equipment or at the facility’s main switchboard(s).
The below diagram shows how power factor correction can provide significant savings in energy consumption and the current drawn from the distribution network.
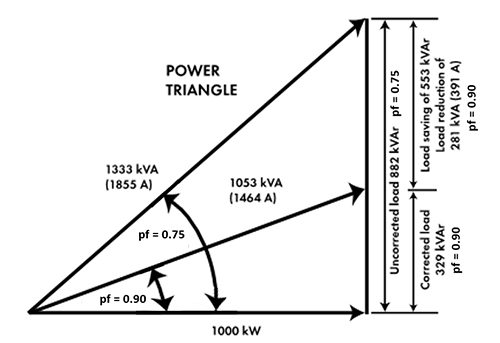
There are a number of issues that require consideration including the design, condition and age of the electrical infrastructure and in particular the switchboard(s), the availability and suitability of space for the new equipment and its connections, and the potential to create or exacerbate harmonics in the electrical supply in the facility which can have serious effects on the operation and life of electrical equipment.
Additional initiatives
There are a number of other ways by which facilities can further reduce their power factor or be made more energy efficient including:
For more information on power factor correction please contact us.
download pdf
July 10, 2018 in Advisory Notes
Heat pumps are a well-established technology that can provide a pathway toward on-site carbon neutrality not possible in buildings that rely on gas fo...

June 1, 2018 in News
A.G. Coombs recently hosted our fifth Canberra event series at the iconic National Museum of Australia. The event attracted over 40 leaders in the bui...

August 23, 2016 in Advisory Notes
Advances in digital technology are providing valuable information to help improve the operation and maintenance of installed building systems includin...

June 2, 2016 in News
A.G. Coombs is contributing to Ideaction 2016 with presentations focused on the use of new and innovative technologies and the opportunities these wil...