
June 1, 2018 in News
Canberra Event Series - Issues, Risks and Opportunities...
A.G. Coombs recently hosted our fifth Canberra event series at the iconic National Museum of Australia. The event attracted over 40 leaders in the bui...
July 10, 2018
Heat pumps are a well-established technology that can provide a pathway toward on-site carbon neutrality not possible in buildings that rely on gas for heating. Electricity used to drive heat pumps can be sourced from renewable or Carbon neutral sources. In some parts of Europe heat pumps are the most popular form of heating.
Why Heat Pumps?
There are a number of factors behind the increasing application of heat pumps for heating:
How they Work
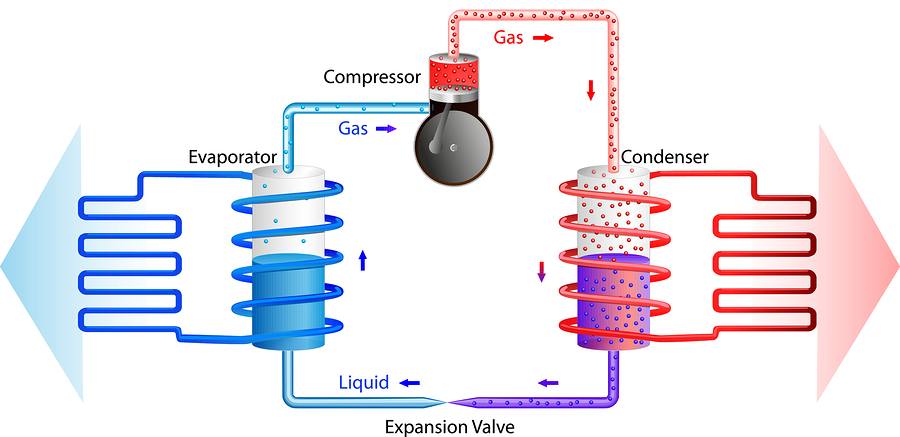
Heat pumps work on the same principle as a refrigerator or air-conditioner. These technologies transfer heat from one place (a lower temperature “heat reservoir” or source) to another (a higher temperature “heat sink”).
A heat pump transfers heat by circulating refrigerant between two heat exchange coils. In one coil, called the “evaporator”, liquid refrigerant evaporates to a vapour at low pressure and in doing so, absorbs heat from its surroundings (the heat source). An electrically driven compressor then pumps this gaseous refrigerant to the other “condenser” coil under high pressure, where the refrigerant condenses back to a liquid and releases the heat energy it absorbed earlier in the cycle to the heat sink. An expansion device then lowers the refrigerant pressure and the cycle is repeated.
Types of Heat Pumps
There are several types of heat pumps available:
Each type of heat pump can transfer heat from its respective heat source to either air (for direct space heating), domestic hot water or heating hot water. Heat pumps are typically low maintenance devices requiring similar attention as for direct expansion air conditioners.
Applications and Opportunities
Traditional building heating hot water systems rely on supply water temperatures between 60-80°C. Until recently, heat pumps have produced comparatively low leaving water temperatures of 40-55°C. Recent developments have seen heat pumps supply water temperatures above 60°C, with some water-to-water heat pumps capable of producing water temperatures up to 85°C.
The successful application of heat pump technology is dependent on site specific characteristics. It is recommended that an engineering analysis is performed to identify technical feasibility and assess financial viability.
Heat pumps are now a viable option that can be considered in many applications for producing heating hot water for space heating and can also deliver domestic hot water. Their high efficiency and potential to use Carbon neutral electricity can make them particularly attractive.
download pdf
June 1, 2018 in News
A.G. Coombs recently hosted our fifth Canberra event series at the iconic National Museum of Australia. The event attracted over 40 leaders in the bui...

August 23, 2016 in Advisory Notes
Advances in digital technology are providing valuable information to help improve the operation and maintenance of installed building systems includin...

July 19, 2016 in Advisory Notes
New electrical network tariff charges will encourage many businesses to review energy usage and ways they can reduce their operational costs.

June 2, 2016 in News
A.G. Coombs is contributing to Ideaction 2016 with presentations focused on the use of new and innovative technologies and the opportunities these wil...